

Science makes it known,
Engineering makes it work,
Art makes it beautiful.
Structure and Elements of a Pascal Program
{ } : multiple statements - 0 or more
< > : indicates token
[ ] : optional
program <program-name> (INPUT,OUTPUT);
{<specification section>}
procedure A;
procedure B;
begin
{<executable-statements>}
A;
{<executable-statements>}
B;
{<executable-statements>}
end.
(the
Free Pascal
compiler does not require (INPUT,OUTPUT);
other compilers may; as always, refer to your compiler
documentation)
unit <unit-name>
interface
{<public specification section>}
{<External Declaration section>}
{<public Procedure Header section>}
implementation
{<private specification section>}
{<functions & procedures section>}
end.
(the <functions & procedures section>
consists of the full Pascal Procedures and Functions
bodies;
see
NumRecGlbl.pas
in
D .dll Calling Free Pascal .dll - Pascal Files
and
Lazarus, Free Pascal, Silverfrost FTN95, and Numerical Recipes
for examples of an Object Pascal Unit)
fnameIO.pas
(see below) is another example of a Pascal unit. It uses
three units
(Windows for
MAX_PATH, HWnd;
SysUtils for
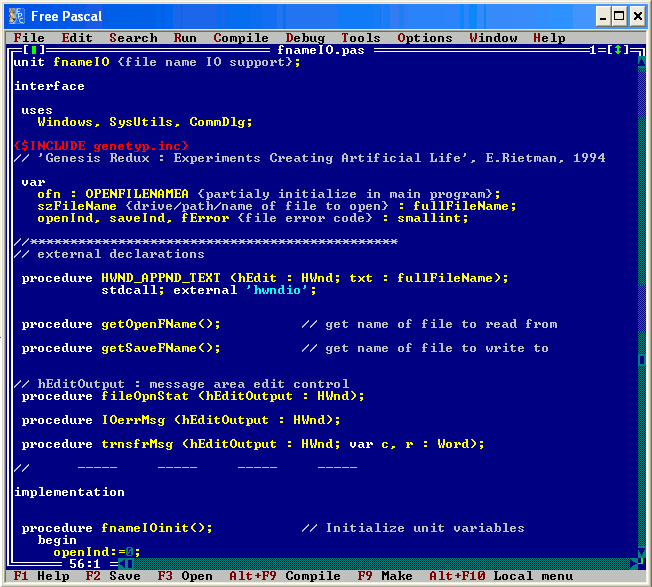
library <library-name>
{<specification section>}
{<External Declaration section>}
{<functions & procedures section>}
exports
{<function-name>
[, <procedure-name> [,...]];}
end.
(to avoid any confusion, <function-name>s
do not need to be grouped together or before
<procedure-name>s in the
exports list or the main body; shown like this
as a matter of convenience; functions and procedures in
the exports list will need
a <call-model> (see below);
Object Pascal Librarys compiles into a Windows .dll;
see
ALlazrs.pas
in
D .dll Calling Free Pascal .dll - Pascal Files
for an example of an Object Pascal Library with external declarations)
procedure <procedure-name> [(<formal-parameter-list>)];
- OR -
function <function-name> [(<formal-parameter-list>)]
: <result-type>;
(placed in a Pascal Unit's Interface; those procedures
and functions are then public to any Pascal Program, Library, or Unit that
uses the Unit)
procedure <procedure-name> [(<formal-parameter-list>)];
<call-model>;
external '<dll-file-name>';
- OR -
function <function-name> [(<formal-parameter-list>)]
: <result-type>;
<call-model>;
external '<dll-file-name>';
(do not include extension in
'<dll-file-name>'; file must be in current
directory or path)
procedure <procedure-name> [(<formal-parameter-list>)];
[<call-model>;]
{<local specification section>}
begin
{<executable-statements>}
end;
(<call-model> used
in Pascal Libraries, together with the Export clause, to declare the
functions and procedures to be exported; also used in
<External Declaration>)
function <function-name> [(<formal-parameter-list>)]
: <result-type>; [<call-model>;]
{<local specification section>}
begin
{<executable-statements>}
<function-name>:=<expression>
end;
<procedure-name> [(<actull-parameter-list>)];
Uses
Windows, Strings;
(use in Program, Unit, and Library
<specification section>, not Functions'/Procedures'
<local specification section>;
Windows
and Strings are external
<unit>s
)
Label
999
(use only in
Functions'/Procedures'
<local specification section>)
const
Max = 10;
Pi = 3.1415926535;
Small = 1e-20;
type
Subs = 1..Max;
VECTOR = array[1..5] of real;
MATRIX = array[1..5,1..5] of real;
POINTER = array[Subs] of integer;
STATUS = (Done,Iterating,Working);
WORDS = string[80];
nrgSubString = array[0..255] of Char;
var
Column,I,J: integer;
A0,B0,Max,X,Y: real;
Flag: boolean;
V,R: VECTOR;
A,D: MATRIX;
Row: POINTER;
Name: string[80];
Lines: WORDS;
State: STATUS;
iErr: smallint;
sNR: single;
(see
Variable Storage Compatibility and Equivalency
for more information on data types;
often const,
type, and occasionally
var are grouped together into include files
- *.inc - and are included with the statement
X := A[1] + 3;
Y := A*X*X + B*X + C;
Flag := true;
Name := 'Fran';
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| div | Integer Division |
| mod | Remainder (Integer) |
(unlike FORTRAN, there is not a ** exponentiation operator)
| = | Equal To |
| <> | Not equal to |
| < | Less than |
| > | Greater than |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| not | Complement |
| and | True if both operands are true |
| or | True if either (or both) operands are true |
true
false
{This is a comment.}
// Also a comment
100:
(labels must be declared in a <specification-statement>)
goto 100;
Warning. Do not use the goto statement to transfer into a If (Block) Control Statement, Indexed Loop Control Statement,
Performs the series of {<executable-statements>} following it or transfers control to an else, or end statement, depending on the value of the <logical-expression>.
if <logical-expression> then
<executable-statement>;
if <logical-expression> then
begin
{<executable-statements>}
end;
if <logical-expression> then
begin
{<executable-statements>}
end
else
begin
{<executable-statements>}
end;
if ((argc[1] = 'T') or (argc[1] = 't'))
and ((argc[2] = 'H') or (argc[2] = 'h')) then
begin
s:=treeHtSwitch;
k:=3
end;
for <index-variable> := <start> to <end> do
<executable-statement>;
for <index-variable> := <start> to <end> do
begin
{<executable-statements>}
end;
for i:=1 to N do
begin
x:=R[i];
B[i]:=YBELL (x, AVE, SDEV)
end;
The <logical-expression> is evaluated first. If the <logical-expression> is true, then the loop body will be executed. The sequence is repeated as long as the expression remains true. If the expression is false, then the loop body will be skipped, and execution will continue with the statement following end;.
while <logical-expression> do
begin
{<executable-statements>}
end;
while SendMessage (hEditOutput, WM_GETTEXTLENGTH, 0, 0) > 8192 do
begin
rmv0_1023 (hEditOutput);
end;
case <logical-expression> of
<constant> : {<executable-statements>}
<constant> : {<executable-statements>}
<constant> : {<executable-statements>}
else
{<executable-statements>}
end;
(<constant> can be of the following types : enumeration types, Ordinal types (except boolean), and chars or string types;
this also includes smallint)
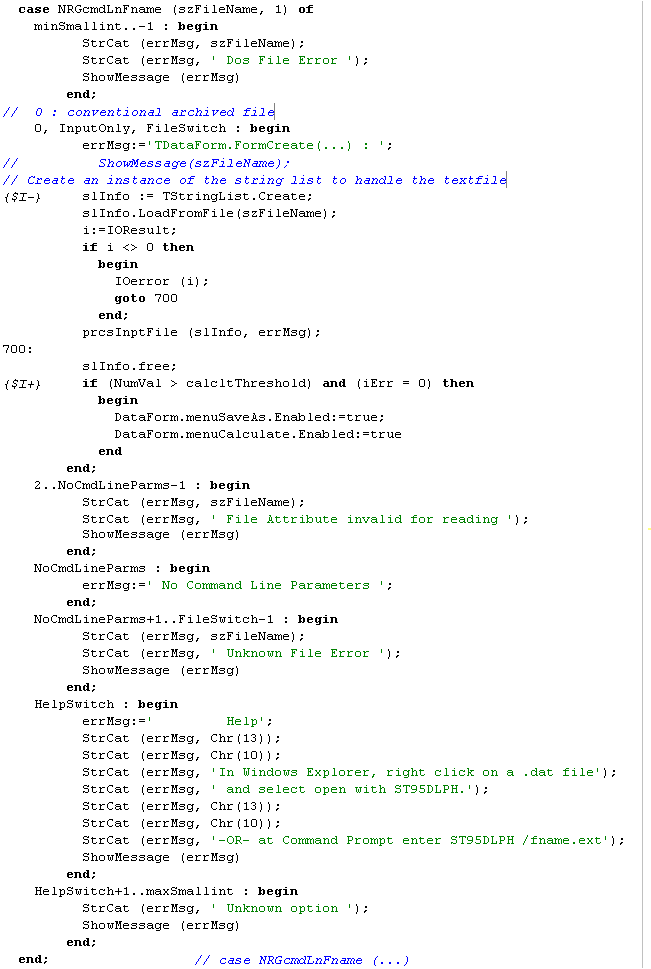
(extreme Object Pascal example demonstrating <case-statement>;
<logical-expression> is the result of function NRGcmdLnFname (...) in Object Pascal Unit NumRecGlbl.pas;
note that <constant> can also be a range - minSmallint..-1, or list of individual values - 0, InputOnly, FileSwitch)
(console I/O)
readln(x,y);
readln(A[i,j]);
writeln;
writeln('x = ',x,' y = ',y);
write ('A(i,j) = ',A[i,j]:15:5);
(file I/O)
Assign (<file-variable>, <file-name>); (assign name of external file to file variable)
Reset (<file-variable>, <record-size>); (open existing file)
BlockRead (<file-variable>, <record-buffer>, <records-to-read-size>, <records-read-size>);
Rewrite (<file-variable>, <record-size>); (open file for writing)
BlockWrite (<file-variable>, <record-buffer>, <records-to-write-size>, <records-written-size>);
(there are additional procedures availble for file I/O; refer to your compiler documentation)
| cos(x) | cosine (radians) |
| sin(x) | sine (radians) |
| exp(x) | exponential exp(x) |
| arctan(x) | inverse tangent (radians) |
| ln(x) | natural logarithm base e |
| sqrt(x) | square root |
| sqr(x) | the square of a number |
| abs(x) | absolute value |
| int(x) | conversion to integer |
| trunc(x) | conversion to integer; no rounding |
| round(x) | the closest integer value |
1. Rietman, Edward (1994). Genesis Redux: Experiments Creating Artificial Life. Windcrest (McGraw-Hill).

